What Is The Prostate?
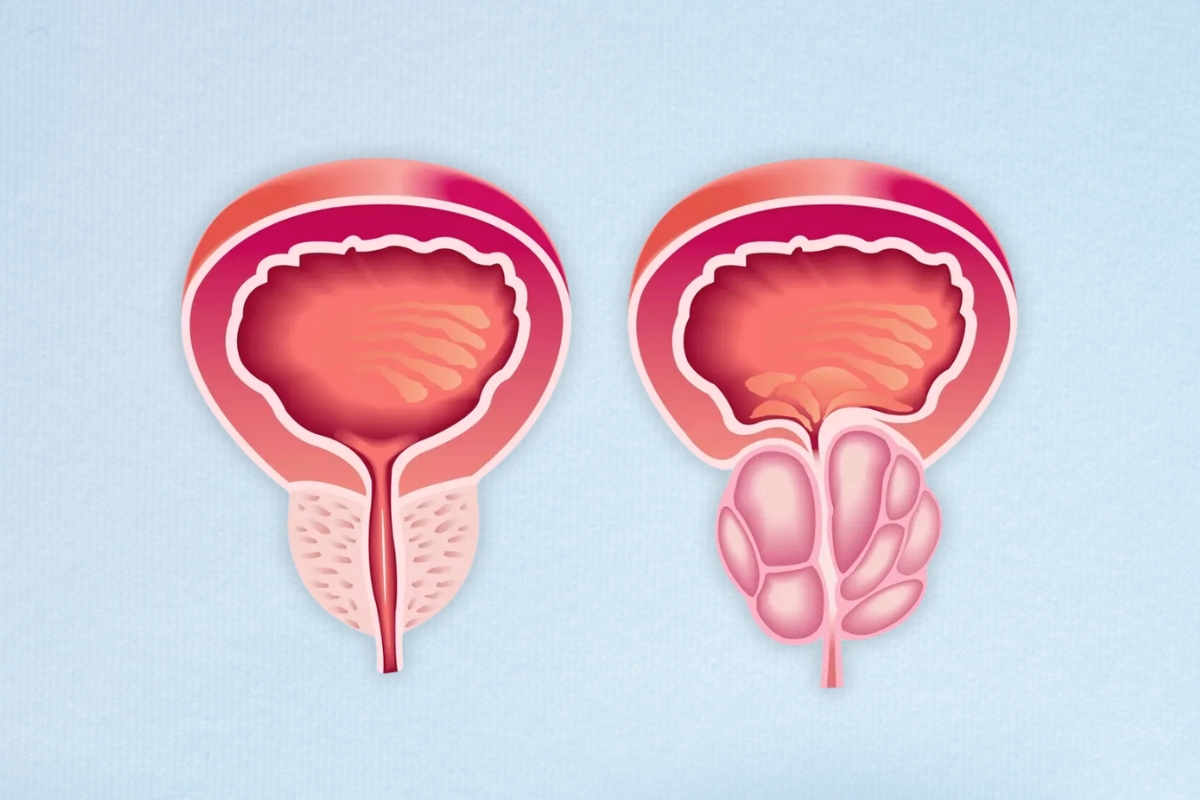
The prostate is a small gland that plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. Despite its small size, about the size of a walnut, it has a significant impact on men's health, particularly as they age. Understanding what the prostate is, its functions, and the common health issues associated with it can help men take proactive steps towards maintaining their prostate health.
Anatomy of the Prostate
The prostate gland is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine and semen exit the body. The prostate is divided into several zones, including the peripheral zone, central zone, and transitional zone, each with specific roles and susceptibility to different conditions.
Functions of the Prostate
The primary function of the prostate is to produce a fluid that, together with sperm cells from the testicles and fluids from other glands, makes up semen. This prostatic fluid is crucial for fertility and reproductive health. It performs several vital functions:
- Nourishment: The fluid produced by the prostate contains enzymes, proteins, and minerals that nourish and protect sperm.
- Protection: The fluid has a slightly alkaline pH, which helps to neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract, protecting sperm and aiding their longevity and motility.
- Transportation: The muscular nature of the prostate also helps propel semen through the urethra during ejaculation.
Common Prostate Issues
As men age, the prostate can be prone to several common conditions, including:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): This is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, common in older men. It can lead to symptoms like frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, weak urine stream, and the feeling of not completely emptying the bladder.
- Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate, which can be either acute or chronic. Symptoms may include pelvic pain, discomfort during urination, and flu-like symptoms in the case of bacterial prostatitis.
- Prostate Cancer: One of the most common cancers in men, particularly those over the age of 50. Early stages often have no symptoms, but advanced stages can cause urinary problems, blood in urine or semen, and pelvic discomfort.
Maintaining Prostate Health
Maintaining a healthy prostate is essential for overall well-being and quality of life. Here are some tips to promote prostate health:
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine screenings and prostate exams, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test and digital rectal exams (DRE), can help detect prostate issues early.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support prostate health. Foods high in antioxidants, such as tomatoes (rich in lycopene) and green tea, are particularly beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of prostate problems.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the urinary system healthy and functioning properly.
- Avoiding Excessive Alcohol and Smoking: Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding smoking can reduce the risk of prostate issues.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination (especially at night), pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, or blood in urine or semen, it's essential to see a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment of prostate issues can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
Conclusion
The prostate may be a small gland, but its importance in men's health cannot be overstated. Understanding its function, common issues, and ways to maintain its health is crucial for preventing potential problems. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and being mindful of any changes in urinary or reproductive health can help men take control of their prostate health and ensure they lead a healthy, active life.
